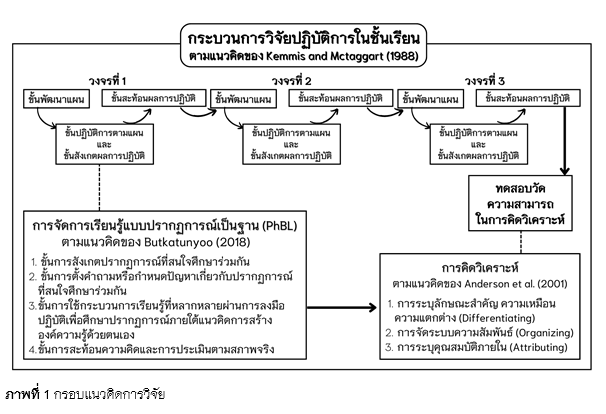
การพัฒนาความสามารถในการคิดวิเคราะห์ของนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 1 โดยการจัดการเรียนรู้แบบปรากฏการณ์เป็นฐาน
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อ 1) ศึกษาความสามารถในการคิดวิเคราะห์ของนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 1 ที่เรียนรู้โดยการจัดการเรียนรู้แบบปรากฏการณ์เป็นฐาน 2) พัฒนาความสามารถในการคิดวิเคราะห์ของนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 1 โดยการจัดการเรียนรู้แบบปรากฏการณ์เป็นฐานจำนวนไม่น้อยกว่าร้อยละ 70 ผ่านเกณฑ์ร้อยละ 70 และ 3) ศึกษาความคิดเห็นของนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 1 ที่มีต่อการจัดการเรียนรู้แบบปรากฏการณ์เป็นฐาน กลุ่มเป้าหมายคือนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 1 ที่กำลังศึกษาอยู่ในภาคเรียนที่ 1 ปีการศึกษา 2565 โรงเรียนเทศบาลวัดกลาง จำนวน 36 คน ได้มาโดยการเลือกแบบเจาะจง เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการวิจัย ได้แก่ 1) แผนการจัดการเรียนรู้แบบปรากฏการณ์เป็นฐาน จำนวน 6 แผน 6 ชั่วโมง 2) แบบบันทึกผลการจัดการเรียนรู้ 3) แบบทดสอบวัดความสามารถในการคิดวิเคราะห์ท้ายวงจรปฏิบัติการ 4) แบบทดสอบวัดความสามารถในการคิดวิเคราะห์ และ 5) แบบสอบถามความคิดเห็นต่อการจัดการเรียนรู้แบบปรากฏการณ์เป็นฐาน วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลเชิงปริมาณโดยหาค่าร้อยละ ค่าเฉลี่ย และค่าส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน และวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลเชิงคุณภาพโดยใช้การวิเคราะห์เนื้อหา
ผลการวิจัย พบว่า 1) นักเรียนที่เรียนรู้โดยการจัดการเรียนรู้แบบปรากฏการณ์เป็นฐานมีคะแนนเฉลี่ยความสามารถในการคิดวิเคราะห์ 19.25 คะแนน จากคะแนนเต็ม 30 คะแนน คิดเป็นร้อยละ 64.17 2) นักเรียนที่เรียนรู้โดยการจัดการเรียนรู้แบบปรากฏการณ์เป็นฐานมีคะแนนความสามารถในการคิดวิเคราะห์ผ่านเกณฑ์ร้อยละ 70 จำนวน 27 คน คิดเป็นร้อยละ 75 สูงกว่าเกณฑ์ที่กำหนดร้อยละ 70 และ 3) นักเรียนมีความคิดเห็นต่อการจัดการเรียนรู้แบบปรากฏการณ์เป็นฐานในภาพรวมเห็นด้วยอยู่ในระดับมากที่สุด
Downloads
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Anderson, L. R., Krathwohl, D. R., Airasian, P. W., Cruikshank, K. A., Mayer, R. E., Pintrich, P. R., … , Wittrock, M. C. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives: Complete edition. New York: Longman.
Armstrong, T., Rockloff, M., Browne, M., and Blaszczynski, A. (2020). Beliefs about gambling mediate the effect of cognitive style on gambling problems. Journal of Gambling Studies, 36, 871–886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-020-09942-5
Auppatham, R. and Poonpaiboonpipat, W. (2021). The case-based learning activities to enhance analytical thinking ability on ratio, proportion and percent for grade-7 students. Journal of Science and Science Education, 4(1), 84–95. Retrieved from https://so04.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JSSE/article/view/251029 [In Thai]
Buranasen, R. (2020). The development of mathematics instructional model based on the constructivist theory to enhance analytical thinking ability of grade 7 students on the topic exponentiation. Journal of Legal Entity Management and Local Innovation, 6(5), 81–97. Retrieved from https://so04.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/jsa-journal/article/view/242136 [In Thai]
Butkatunyoo, O. (2018). Phenomenon based learning for developing a learner’s holistic views and engaging in the real world. Journal of Education Studies Chulalongkorn University, 46(2), 348-365. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/EDUCU/article/view/131909/99030 [In Thai]
Dammak, P., Pana, S., and Boonpook, W. (2022). A study of analytical thinking skill and learning achievement by phenomenon-based learning in social studies subject. Journal of Educational Technology and Communications Faculty of Education Mahasarakham University, 5(15), 36–48. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/etcedumsujournal/article/view/255040 [In Thai]
Iaolek, C. and Anurakwatthana, O. (2022). The effect of phenomenon-based learning experience provision for development critical thinking skill’s pre-service teachers. Journal of Education Silpakorn University, 20(1), 257–273. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/suedujournal/article/view/246759 [In Thai]
Kemmis, S., and Mctaggart, R. (1988). The action research planner: Action research and the critical analysis of pedagogy. (3rd ed.). Geelong: Deakin University Press.
Kuder, G.F. and Richardson, M.W. (1937). The theory of the estimation of test reliability. Psychometrika 2, 151–160. DOI: 10.1007/BF02288391
Kumpanat, T., Koonchayanggoon, S., Punchaariyakun, S., Pinthana, P., and Kasakij, S. (2020). Cognitive learning behavior based on the concept of bloom’s revised taxonomy. Journal of Graduate Research, 11(2), 1–9. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/banditvijai/article/view/242749 [In Thai]
Likert, R. (1932). A technique for the measurement of attitudes. Archives of Psychology, 22(140), 5–55. Retrieved from https://legacy.voteview.com/pdf/Likert_1932.pdf
Mahavijit, P. (2019). Application of phenomenon-based learning and active learning in elementary education course to enhance 21st century learning skills. Journal of Education Khon Kaen University, 42(2), 73–90. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/EDKKUJ/article/view/195627 [In Thai]
Mattila, P., and Silander, P. (Ed.). (2015). How to create the school of the future–revolutionary thinking and design from Finland. Oulu: Multprint. Retrieved from https://www.classter.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/How-to-create-the-school-of-the-future.pdf
Ministry of Education (MOE). (2008). Core indicators and learning strands of Thai language learning area according to basic education core curriculum B.E. 2551 (A.D. 2008). Bangkok: The Agricultural Co-operative Federation of Thailand. [In Thai]
Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC). Office of Secretary to National Strategy Committee. (2018). National Strategy B.E. 2561–2580 (A.D. 2021–2037) (Official Gazette). Bangkok: Office of Secretary to National Strategy Committee, Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council. Retrieved from https://www.nesdc.go.th/download/document/SAC/NS_PlanOct2018.pdf [In Thai]
Silander, P. (2015). Phenomenon based learning. Retrieved from http://www.phenomenaleducation.info/phenomenon-based-learning.html
Soythongdee, S., and Konkitsuwan, N. (2017). The development of analytical thinking in language learning of grade 1 students by problem-based learning (PBL). Journal of Education Khon Kaen University, 40(2), 52–62. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/EDKKUJ/article/view/90417/73852 [In Thai]
Symeonidis, V. and Schwarz, J. F. (2016). Phenomenon-based teaching and learning through the pedagogical lenses of phenomenology: The recent curriculum reform in Finland. In Forum Oświatowe, 28(2), 31-47. Retrieved from https://www.forumoswiatowe.pl/index.php/czasopismo/article/view/458/293
Tachaphol, P., Nantachad, K., and Passago, S. (2021). Development of learning activities by applying inquiry with phenomenal based learning to promote analytical thinking ability and attitude towards science learning of mathayomsuksa 2 students. Udon Thani Rajabhat University Journal of Guru Education, 3(1), 19–36. Retrieved from https://so06.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/edudru/article/view/248916 [In Thai]
Tassaniyom, A., and Chookhampaeng, S. (2020). Developing analytical thinking ability of mathayomsuksa 4 students in biological science using phenomenon-based learning. Journal of MCU Nakhondhat, 7(6), 31–44. Retrieved from https://so03.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JMND/article/view/244521 [In Thai]
The Institute for the Promotion of Teaching Science and Technology (IPST). (2021). PISA 2018 Assessment in Reading, Mathematics and Science. Bangkok: The Institute for the Promotion of Teaching Science and Technology. Retrieved from https://pisathailand.ipst.ac.th/pisa2018-fullreport/ [In Thai]
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). (2019). PISA 2018 assessment and analytical framework. Paris: OECD Publishing. DOI: 10.1787/b25efab8-en
Tubboon, C., and Pansri, O. (2022). The development of critical reading ability of mathayomsuksa 3 students by phenomenon based learning with six thinking hat. Journal of Modern Learning Development, 7(6), 148–158. Retrieved from https://so06.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/jomld/article/view/255064 [In Thai]
Watklang Municipal School. (2021). School Self-Assessment Report (SAR) of Basic Education Level in Academic Year B.E. 2563 (A.D. 2020). Khon Kaen: Watklang Municipal School. (Mimeographed). [In Thai]
Wongsom, J. and Pankaew, P. (2016). Science learning management through inquiry method with graphic organizers to develop analytical thinking ability of prathomsuksa 6 students. Journal of Graduate Research, 7(2), 47–59. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/banditvijai/article/view/96239 [In Thai]
Yusoff, M. S. B. (2019). ABC of content validation and content validity index calculation. Education in Medicine Journal, 11(2), 49–54. DOI: 10.21315/eimj2019.11.2.6