ประเมินประสิทธิผลของสื่อการสอนสำหรับการประมาณเวลาขึ้น-ตกของดาวเคราะห์
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
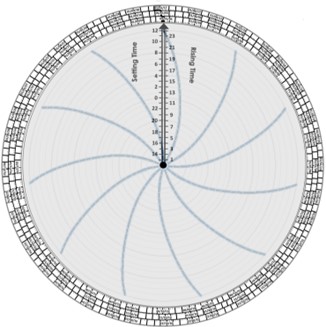
ในงานวิจัยที่ผ่านมาสื่อการสอนสำหรับการประมาณเวลาขึ้น-ตกของดาวเคราะห์ (PARST) ได้ถูกออกแบบและสร้างขึ้นโดยมีจุดมุ่งหมายที่จะยกระดับประสบการณ์การเรียนรู้ของนักเรียนในเรื่องการเคลื่อนที่ของดาวเคราะห์ งานวิจัยนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อประเมินประสิทธิผลการเรียนรู้ของสื่อการสอนกับนักเรียน 3 กลุ่ม ในห้องเรียน อันได้แก่ (1) กลุ่มที่ใช้เฉพาะสื่อการสอน (2) กลุ่มที่ได้รับการสอนเกี่ยวกับการเคลื่อนที่ของดาวเคราะห์โดยไม่ใช้สื่อการสอน (3) กลุ่มที่ได้รับการสอนเกี่ยวกับการเคลื่อนที่ของดาวเคราะห์และใช้สื่อการสอน แบบทดสอบก่อนเรียนและหลังเรียนที่ถูกออกแบบตามอนุกรมวิธานของบลูมได้ถูกนำมาใช้เพื่อประเมินนักเรียนทั้งสามกลุ่ม โดยมีวิธีการประเมินผลจากการทำแบบทดสอบก่อนและหลังเรียน สี่วิธี ได้แก่ (a) การทดสอบสมมติฐาน (b) ขนาดของผล (c) ผลการเรียนรู้ที่เพิ่มขึ้น และ (d) ระดับความยาก การประเมินทั้งสี่วิธีแสดงผลในรูปแบบเดียวกันของความมีประสิทธิภาพสูงสุดในกลุ่มนักเรียนที่ใช้สื่อการสอนอย่างเดียวโดยไม่ได้รับการสอนเกี่ยวกับการเคลื่อนที่ของดาวเคราะห์ ผลการวิจัยนี้สื่อเป็นนัยว่าการใช้สื่อการสอนโดยไม่ได้เรียนเกี่ยวกับเวลาขึ้นและตกของดาวเคราะห์สามารถกระตุ้นให้นักเรียนพัฒนาความเข้าใจเกี่ยวกับการเคลื่อนที่ของดาวเคราะห์ได้
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Abdulwahed, M., & Nagy, Z. (2009). Applying Kolb's Experiential Learning Cycle for Laboratory Education. Journal of Engineering Education, 98.
Bakas, C., & Mikropoulos, T. (2003). Design of virtual environments for the comprehension of planetary phenomena based on students' ideas. International Journal of Science Education, 25, 949 - 967.
Bardar, E. M. (2007). First results from the light and spectroscopy concept. Astronomy Education Review, 6(2), 75-84.
Barnett, M. L., & Mathisen, A. (1997). Tyranny of the p-value: the conflict between statistical significance and common sense. Journal of dental research, 76(1), 534–536.
Bloom, B. S. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives. Longman green and co LTD, England.
Boopathiraj, C., & Chellamani, D.K. (2013). Analysis of test items on difficulty level and discrimination index in the test for research in education. International Journal of Social Sciences & Interdisciplinary Research, 2, 189-193.
Coe, R. (2012). It's the Effect Size, Stupid What effect size is and why it is important. Paper Presented at the British Educational Research Association Annual Conference, Exeter, England, UK. 2002
Cohen, A. (2022). Teaching the astronomical visualization used for the explanation of the ancient Ein-Gedi archaeological zodiac and its related inscription. Journal of Astronomy & Earth Sciences Education, 9(2), 25–38.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Lawrence Erlbaum Associate, New York.
Galano, S., Colantonio, A., Leccia, S., Marzoli, I., Puddu, E., & Testa, I. (2018). Developing the use of visual representations to explain basic astronomy phenomena. Physical Review Physics Education Research, 14(1), 010145
Hake, R. R. (1998). Interactive-engagement vs traditional methods: A six-thousand student survey of mechanics test data for introductory physics courses. American Journal of Physics, 66(1), 64-74.
Karaksha, A., Grant, G.D., Nirthanan, S., Davey, A.K., & Anoopkumar‐Dukie, S. (2014). A Comparative Study to Evaluate the Educational Impact of E-Learning Tools on Griffith University Pharmacy Students’ Level of Understanding Using Bloom’s and SOLO Taxonomies. Education Research International, 2014 (2014): 934854-1-934854-11.
Laphirattanakul, A., Wannawichian, S. & Wattanakasiwich, P. (2024). PARST educational tool for planet positioning. The Physics Teacher, 62(4), 272-277.
Nakagawa, S., & Cuthill, I. C. (2007). Effect size, confidence interval and statistical significance: a practical guide for biologists. Biological reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 82(4), 591–605.
Neyman, J. & Pearson, E. S. (1933). On the problem of the most efficient tests of statistical hypotheses. Springer Series in Statistics. Springer, New York, NY.
Ole, F. C. B. (2020). Effect of a developed physics laboratory manual on the conceptual understanding of industrial technology student. European Journal of Education Studies, 7(6), 113-122.
Peralta, J., Prieto, J. A., Orozco-Sáenz, P., González, J., Trujillo, G., Torres, L., Sánchez, A. & Arnedo, M. (2023). Secondary school students observe Venus with NASA Infrared Telescope Facility (IRTF), Research Notes of the AAS, 7(3), 53-57.
Plummer, J.D. (2014). Spatial thinking as the dimension of progress in an astronomy learning progression. Studies in Science Education. 50(1), 1-45.
Rakap, S. (2015). Effect sizes as result interpretation aids in single-subject experimental research: description and application of four non overlap method. British Journal of Special Education, 42(1), 11-33.
Ruangsuwan, C. & Arayathanitkul, K. (2009). A low-cost celestial globe for hands-on astronomy. Physics Educucation, 44(5), 503-508.
Seidel, T., & Shavelson, R. J. (2007). Teaching effectiveness research in the past decade: The role of theory and research design in disentangling meta-analysis results. Review of educational research, 77(4), 454-499
Srisawasdi, N. (2018). Transforming chemistry class with technology-enhanced active inquiry learning for the digital native generation. In C. Cox & W. Schatzberg (Eds.) International Perspectives on Chemistry Education Research and Practice (pp. 221–233). ACS Symposium Series 1142, American Chemical Society: Washington, DC.
Stover, S., & Saunders, G. (2000). Astronomical misconceptions and the effectiveness of science museums in promoting conceptual change. Journal of Elementary Science Education, 12, 41-51.
Sullivan, G. M. & Feinn, R. (2012). Using Effect Size-or Why the P Value Is Not Enough. Journal of Graduate Medical Education, 4(3), 279-282.
Woods, M. & Rosenberg, M. E. (2016). Educational tools: Thinking outside the box. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 11(3), 518-526.
Xu, M., Fralick, D., Zheng, J. Z., Wang, B., Tu, X. M. & Feng, C. (2017) The Differences and Similarities Between Two-Sample T-Test and Paired T-Test. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry, 29(3), 184-188.