Phenomenon Based Learning for Developing Competency in Explaining Scientific Phenomena of the 8th Grade Students About Earth and it’s Change
Main Article Content
Abstract
The purposes of this research were to study: 1) the phenomenon-based learning to develop Scientific Explanation competency about the Earth and changes; and 2) the results of developing competencies in explaining phenomena scientifically. It was action research. The sample group consisted of 13 students of grade 8th, academic year 2022, selected through the purposive sampling. The research instruments consisted of: 1) lesson plans, 2) reflections on learning management, 3) a competency test for explaining scientific phenomena, and 4) a Phenomenon-based learning worksheet. Qualitative data were analyzed by content analysis and verify the accuracy of qualitative data analysis using triangulation using the same data sources (Resource Triangulation). Quantitative data was analyzed by calculating percentages.
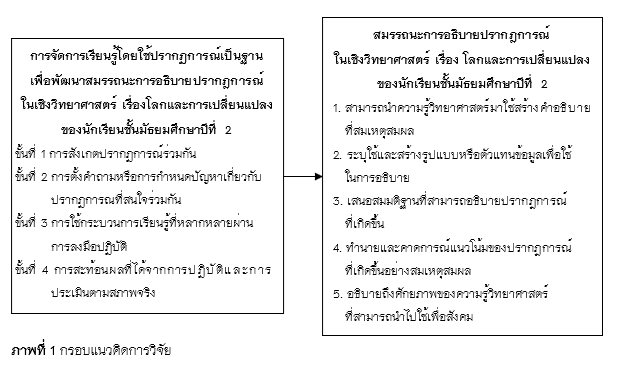
The results of the research found that 1) there were four steps of phenomenon-based learning to develop students’ scientifically competency in explaining phenomena of the grade 8th students about earth and changes consisting of Step 1: Collaborative observation of the phenomena; Step 2: Formulation question and defining problems related to phenomena of common interest; Step 3: Using various learning processes through practice; and Step 4: Reflecting on the results. From doing and evaluating according to actual conditions. 2) the 8th grade students who received phenomenon-based learning about earth and changes had higher ability to explain phenomena in science after studying than before and there has been an improvement in the ability to explain phenomena scientifically.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Boonmaton, R & Supap, W, and Wiriyapong, R. (2017). The development of grade 11 students’ mathematical literacy on probability using context-based learning. Journal of Information and Learning, 29(2), 51-61. Retrieved from https://journal.oas.psu.ac.th/index.php/asj/article/view/1250/1091 [In Thai]
Bualombai, S., Sirithanyarat, C., and Saengloetuthai, J. (2023). The development of explaining phenomena scientifically competence of grade 5 students through phenomenon-based learning management. Journal for Social Sciences Research, 14(1), 57-76. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/ssr/article/view/260258 [In Thai]
Butkatunyoo, O. (2018). Phenomenon based learning for developing a learner’s holistic views and engaging in the real world. Journal of Education Studies, 46(2), 348–365. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/EDUCU/article/view/131909/99030 [In Thai]
Chaiwon, T. and Nugultham, K. (2021). Phenomenon -based learning: Integrated learning for enhancing learners' knowledge in the real world. Journal of Graduate Studies Valaya Alongkorn Rajabhat University, 15(2), 251-263. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JournalGradVRU/article/download/246642/168302/893967 [In Thai]
Kongkoey, T. (2018). Development of grade 10 students’ learning progression for ecosystem through adaptive instruction. (Master of Education, Science Education Kasetsart University).
Ladachart, L. and Ladachart, L. (2018). Formative assessment: A gateway to science teachers’ professional growth and science education reform. Journal of Research Unit on Science, Technology and Environment for Learning, 9(2), 297-323. Retrieved From https://ejournals.swu.ac.th/index.php/JSTEL/article/view/9733 [In Thai]
Mahavijit, P. (2017). Phenomenal learning from Finland. IPST Magazine, 46(209), 40-45. Retrieved from https://emagazine.ipst.ac.th/209/#40 [In Thai]
Nielsen, V., & Davies, A. (2018). The what, why, and how of phenomenon-based learning. Retrieved from https://www.onatlas.com/blog/phenomenon-based-Learning [In Thai]
Pengpajon, P. and Chanunan, S. (2023). Implement phenomenon base learning to enhance scientific literacy of 11th grade students involving acid-base topic. Journal of Roi Kaensarn Academi, 8(9), 248-262. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JRKSA/article/view/262842 [In Thai]
The Institute for the Promotion of Teaching Science and Technology (IPST). (2018). The result of PISA 2015 is reading and map excellence and justice for students (PISA 2015 results) excellence and equality in education) by neighbors for cooperation forgotten and overlooked. The Institute for the Promotion of Teaching Science and Technology.
Promyod, N. (2019). Generating scientific explanations through the CER learning process (Claim, Evidence and Reasoning). IPST Magazine, 47(219), 11-15. Retrieved from https://emagazine.ipst.ac.th/219/10/ [In Thai]
Saengchan, S. and Kijkuakul, S. (2023). Phenomenon-based learning approach promoting scientific literacy on the buoyancy of liquids for 8th grade students. Journal of Roi Kaensarn Academi, 8(9), 55-73. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JRKSA/article/view/262762 [In Thai]
Suwarat, K. (2021). Development of science communication of 11 grade ethnically diverse student using phenomenon – based learning in topic of respiratory system. (Master’s thesis, Department of Science Education, Naresuan University). [In Thai]
Symeonidis, V. and Schwarz, J. F. (2016). Phenomenon-based teaching and learning through the pedagogical lenses of phenomenology: The recent curriculum reform in Finland. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313696751_Phenomenon-Based_Teaching_and_Learning_through_the_Pedagogical_Lenses_of_Phenomenology_The_Recent_Curriculum_Reform_in_Finland [In Thai]
Tamtrakul, P. and Bongkotphet, T. (2022). Developing scientific literacy through context-based learning with technology involving acid-base topics for 11th grade students. Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences Nakhon Phanom University, 12(1), 291-305. Retrieved from https://so03.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/npuj/article/download/252423/173015/964175 [In Thai]
Thammawongsa, B. (2019). Encourage children to think critically teachers had to stop asking if they understood and not rush to give answers. Retrieved from https:/thepotential.org/knowledge/teaching-critical-thinking
Worawattananon, S. and Chanunan, S. (2022). Phenomenon-based learning management to develop critical thinking and problem solving skills on the phenomenon of the world and natural disasters of grade 6 students. Journal of Roi Kaensarn Academi, 8(1), 136-149. Retrieved from https://so02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JRKSA/article/view/257433. [In Thai]
Yusoff, M. S. B. (2019). ABC of content validation and content validity index calculation. Education in Medicine Journal, 11(2), 49–54. DOI: 10.21315/eimj2019.11.2.6. Retrieved from https://eduimed.usm.my/EIMJ20191102/EIMJ20191102_06.pdf [In Thai]