ผลกระทบของโควิด–19 ต่อพฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคในธุรกิจบริการที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป และแนวทางในการรับมือของผู้ประกอบการธุรกิจบริการ ในกรุงเทพมหานคร และปริมณฑล
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
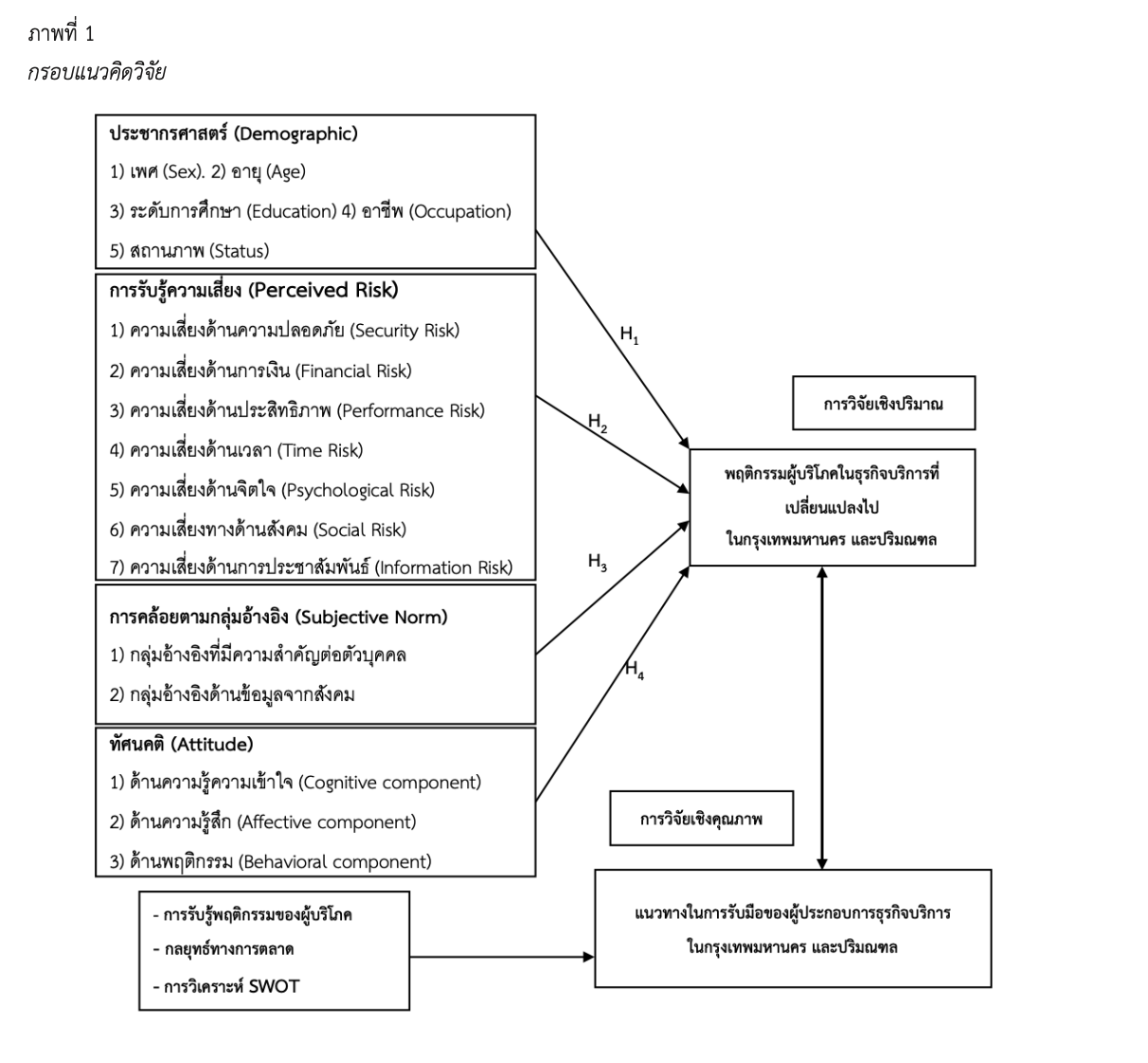
การวิจัยครั้งนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อ 1) เพื่อศึกษาผลกระทบโควิด-19 ต่อพฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคในธุรกิจบริการที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป ในกรุงเทพมหานคร และปริมณฑล จำแนกตามปัจจัยด้านประชากรศาสตร์ 2) เพื่อศึกษาผลกระทบโควิด-19 ในส่วนของการรับรู้ความเสี่ยง การคล้อยตามกลุ่มอ้างอิง และทัศนคติ ที่มีอิทธิพลต่อพฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคในธุรกิจบริการที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป ในกรุงเทพมหานคร และปริมณฑล และ 3) เพื่อศึกษาแนวทางในการรับมือพฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป ของผู้ประกอบการธุรกิจบริการ ในกรุงเทพมหานคร และปริมณฑล ใช้รูปแบบการวิจัยแบบผสมผสาน แบบขั้นตอนเชิงอธิบาย กลุ่มตัวอย่างเป็น ประชากรทั่วไปที่มีอายุตั้งแต่ 18 ปีขึ้นไป ทั้งเพศชาย หญิง และกลุ่มที่มีความหลากหลายทางเพศ (LGBTQIA+) จำนวน 400 คน และผู้ให้ข้อมูลสำคัญที่เป็นผู้ประกอบการธุรกิจบริการจำนวน 10 ธุรกิจ เก็บข้อมูลพื้นที่กรุงเทพมหานคร และปริมณฑล รวบรวมข้อมูลโดยแบบสอบถาม และแบบสัมภาษณ์ สถิติที่ใช้ในวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลเชิงพรรณนา ได้แก่ การหาค่าร้อยละ ค่าเฉลี่ย ค่าเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน และสถิติที่ใช้ในการวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลเชิงอนุมาน ได้แก่ การวิเคราะห์ความแปรปรวนทางเดียว และการวิเคราะห์สถิติการถดถอยเชิงเส้น
ผลการศึกษาพบว่า
กลุ่มตัวอย่างจากแบบสอบถามเป็นเพศหญิงอายุระหว่าง 36–45 ปี อาชีพพนักงานบริษัทเอกชน/ลูกจ้าง การศึกษาระดับปริญญาตรี สถานภาพสมรส สมมติฐานงานวิจัย พบว่า ลักษณะประชากรศาสตร์ในด้านอาชีพ และการศึกษา ส่งผลต่อพฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคในธุรกิจบริการที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป ในกรุงเทพมหานคร และปริมณฑล แตกต่างกัน อย่างมีนัยสำคัญที่ 0.05 ในส่วนของผลกระทบโควิด-19 ในส่วนของการรับรู้ความเสี่ยงด้านความปลอดภัย การเงิน สังคม และการประชาสัมพันธ์ และในส่วนของการคล้อยตามกลุ่มอ้างอิงด้านข้อมูลจากสังคม และในส่วนของทัศนคติในทุกด้าน มีอิทธิพลต่อพฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคในธุรกิจบริการที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป ในกรุงเทพมหานคร และปริมณฑล อย่างมีนัยสำคัญที่ 0.05 และผู้ให้ข้อมูลสำคัญ พบว่า การใช้บริการออนไลน์เพิ่มขึ้น ลดการใช้บริการที่สามารถทำเองได้ ลดความถี่ในการเข้าใช้บริการ เลือกใช้บริการไปที่บ้านแบบส่วนตัว หาข้อมูลเพิ่มขึ้นก่อนรับบริการ และเมื่อวิเคราะห์ SWOT พบว่า จุดแข็ง คือ เป็นเจ้าของสถานที่ มีสินค้าจำหน่ายในช่วงที่ปิดกิจการ จุดอ่อน คือ ไม่มีเงินทุนเพียงพอต่อค่าใช้จ่ายที่เกิดขึ้น โอกาส คือ มีบริการบางส่วนผลตอบรับเพิ่มขึ้น จากพฤติกรรมการอยู่บ้าน และอุปสรรค คือ นโยบายต่าง ๆ ของภาครัฐ และในอนาคตผู้ประกอบการให้ความสำคัญกับกลยุทธ์ช่องทางการจัดหน่าย โดยเฉพาะช่องทางออนไลน์ที่คาดว่ามีบทบาทในอนาคต และผู้ประกอบการมีแนวทางในการรับมือพฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป โดยใช้ราคา และโปรโมชั่นเข้ามาจูงใจ สร้างความเข้าใจให้ผู้บริโภครู้สึกว่าบริการสามารถจับต้องได้ เพิ่มตัวเลือกบริการให้หลากหลาย และค่อย ๆ ปรับธุรกิจให้มีความสอดคล้องกับพฤติกรรมของผู้บริโภค
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
** ข้อความ ข้อคิดเห็น หรือข้อค้นพบ ในวารสารสหวิทยาการสังคมศาสตร์และการสื่อสารเป็นของผู้เขียน ซึ่งจะต้องรับผิดชอบต่อผลทางกฎหมายใด ๆ ที่อาจเกิดขึ้นจากบทความและงานวิจัยนั้น ๆ โดยมิใช่ความรับผิดชอบของคณะนิเทศศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏรำไพพรรณี **
เอกสารอ้างอิง
ชาญชัย ชัยประสิทธิ์. (2564, พฤศจิกายน 14). เจาะพฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคไทยที่เปลี่ยนไปในยุคโควิด-19. PwC Thailand. https://www.pwc.com/th/en/pwc-thailand-blogs/blog-20210518.html.
ฑิตาพร รุ่งสถาพร. (2563). พฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคต่อการซื้อสินค้าบนช่องทางออนไลน์ในภาวะวิกฤตโควิด-19 ในเขต กรุงเทพมหานคร ปริมณฑล และพิษณุโลก. การค้นคว้าอิสระปริญญานิเทศศาสตร์มหาบัณฑิต สาขาวิชา การสื่อสารการตลาดดิจิทัล. มหาวิทยาลัยกรุงเทพ
ณัธภัชร เฉลิมแดน. (2563). พฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคในการสั่งอาหารแบบเดลิเวอรี่ผ่านโมบายแอปพลิเคชันช่วงเกิดโรคติด เชื้อไวรัสโคโรนาสายพันธุ์ใหม่ 2019 (COVID-19) ในเขตกรุงเทพมหานคร. วารสารบริหารธุรกิจ อุตสาหกรรม, 2(1). https://so03.tci- thaijo.org/ index.php/iba/article/ view/244515
วิสรา ศรีบรรจง และ นันทวัน เหลี่ยมปรีชา. (2564). พฤติกรรมการซื้อสินค้าออนไลน์ของผู้บริโภคภายใต้วิถีความปกติใหม่ (New Normal) ในเขตอำเภอเมือง จังหวัดพิษณุโลก ที่มีผลต่อส่วนประสมการตลาดออนไลน์. โครงการนำเสนอผลงานวิชาการระดับชาติ ประจำปี พ.ศ. 2564 (NPSC 2021) (น. 40-52). มหาวิทยาลัยนเรศวร.
สุขุม เฉลยทรัพย์. (2564, พฤศจิกายน 18). โควิด-19กับพฤติกรรมที่เปลี่ยนไป. สยามรัฐ.https://siamrath.co.th/n/276754.
ศูนย์วิจัยกสิกรไทย. (2564, สิงหาคม 4). Work From Home วิถีการทำงานยุคนี้ ที่ยังต้องหาจุดสมดุล. ศูนย์วิจัยกสิกรไทย. https://kasikornresearch.com/th/analysis/k-social-media/Pages/WFH-FB-04-08-21.aspx.
มนัสชนก ไชยรัตน์. (2563). พฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไปช่วงสถานการณ์ COVID-19 ในพื้นที่กรุงเทพมหานคร. [วิทยานิพนธ์ปริญญามหาบัณฑิต]. มหาวิทยาลัยรามคำแหง. https://mmm.ru.ac.th/MMM/IS/vlt15-1/6114993677.pdf
มหาวิทยาลัยธรรมศาสตร์. (2564, พฤศจิกายน 18). เปิดงานวิจัย “พฤติกรรมของคนที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไปในช่วง COVID - 19” ของนักศึกษาปริญญาโทธรรมศาสตร์. มหาวิทยาลัยธรรมศาสตร์. https://tu.ac.th/thammasat-210164-tbs-research-behavior-people-during-covid-19.
พงศ์พันธ์ อนันต์วรณิชย์ และ ธาดาธิเบศร์ ภูทอง. (2564) ความสัมพันธ์เชิงสาเหตุของความตั้งใจเชิงพฤติกรรม. ของผู้บริโภคในการใช้งานแอปพลิเคชันสั่งอาหารในช่วงสถานการณ์การแพร่ระบาดของโควิด - 19 ในสังคมไทย. วารสารรัชต์ภาคย์, 15(43), 38-55. https://so05.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/RJPJ/article/view/253732.
Ajzen, I. (1991). The Theory of Planned Behaviour: Reactions and Reflections.
Akter, S., Ashrafi, T., & Waligo, V. (2021). Changes in consumer purchasing behavior due to COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Marketing and Consumer Research, 77, 33-46.
Bartik, A. W., Bertrand, M., Cullen, Z. B., Glaeser, E. L., Luca, M., & Stanton, C. T. (2020). How are small businesses adjusting to COVID-19? Early evidence from a survey (No. w26989). National Bureau of Economic Research. https://www.nber.org/papers/w26989
Cochran, W. G. (1977). Sampling techniques (3rd ed.). Wiley
Dannenberg, P., Fuchs, M., Riedler, T., & Wiedemann, C. (2020). Digital transition by COVID‐19 pandemic? The German food online retail. Tijdschrift voor economische en sociale geografie, 111(3), 543-560.
Gursoy, D., & Chi, C. G. (2020). Effects of COVID-19 pandemic on hospitality industry: review of the current situations and a research agenda. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 29(5), 527-529.
Gu, S., Ślusarczyk, B., Hajizada, S., Kovalyova, I., & Sakhbieva, A. (2021). Impact of the covid-19 pandemic on online consumer purchasing behavior. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 16(6), 2263-2281.
Hamdah, D.F., & Garut (2019). The Effect of Attitude, Subjective Norm, and Perceived Behavior Control of Taxpayer Compliance of Private Person in Tax Office Garut, Indonesia. Integrative Business and Economics Research, 9(1), 298-306. http://buscompress.com/uploads/3/4/9/8/34980536/riber_9-s1_23_k19-086_298-306.pdf
Kurtisi , H., & Alver, M. (2021). Online consumer behaviour during a pandemic: A study on the effects of COVID - 19 on online consumers in Sweden. Jönköping International Business School, JIBS, Business Administration. Digitala Vetenskapliga Arkivet. https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1566947/FULLTEXT01.pdf
Szmigiera. (2023, January 17). Impact of the coronavirus pandemic on the global economy - Statistics & Facts. Statista: https://www.statista.com/topics/6139/COVID - 19-impact-on-the-global-economy/#dossierKeyfigures.
Muresan, I. C., Harun, R., Arion, F. H., Brata, A. M., Chereches, I. A., Chiciudean, G. O., ... & Tirpe, O. P. (2021). Consumers’ attitude towards sustainable food consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic in Romania. Agriculture, 11(11), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11111050
NALISA. (2020, เมษายน 15). เทรนด์พฤติกรรมผู้บริโภค-ผู้ประกอบการจะไปต่อทิศทางไหนหลังสถานการณ์ โควิด-19. Marketeer. https://marketeeronline.co/archives/158845.
Nguyen, T. M. A., Nguyen, T. H., & Le, H. H. (2022). Online Shopping in Relationship with Perception, Attitude, and Subjective Norm during COVID-19 Outbreak: The Case of Vietnam. Sustainability, 14(22), 15009. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142215009
PWC. (2021, November 14). The global consumer: Changed for good : PwC’s June 2021 Global Consumer Insights Pulse Survey. PwC. https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/industries/consumer-markets/consumer-insights-survey.html.
Polat, İnci, Erdoğan, D. ., & Sesliokuyucu, O. S. (2021). The Impact of Attitude and Subjective Norm on Airline Passengers’ Travel Intention in the Covid-19 Era: Mediating Role Of Perceived Risk. Anais Brasileiros De Estudos Turísticos, 11. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5770983
Sheth, J. (2020). Impact of Covid-19 on consumer behavior: Will the old habits return or die?. Journal of business research, 117, 280-283.