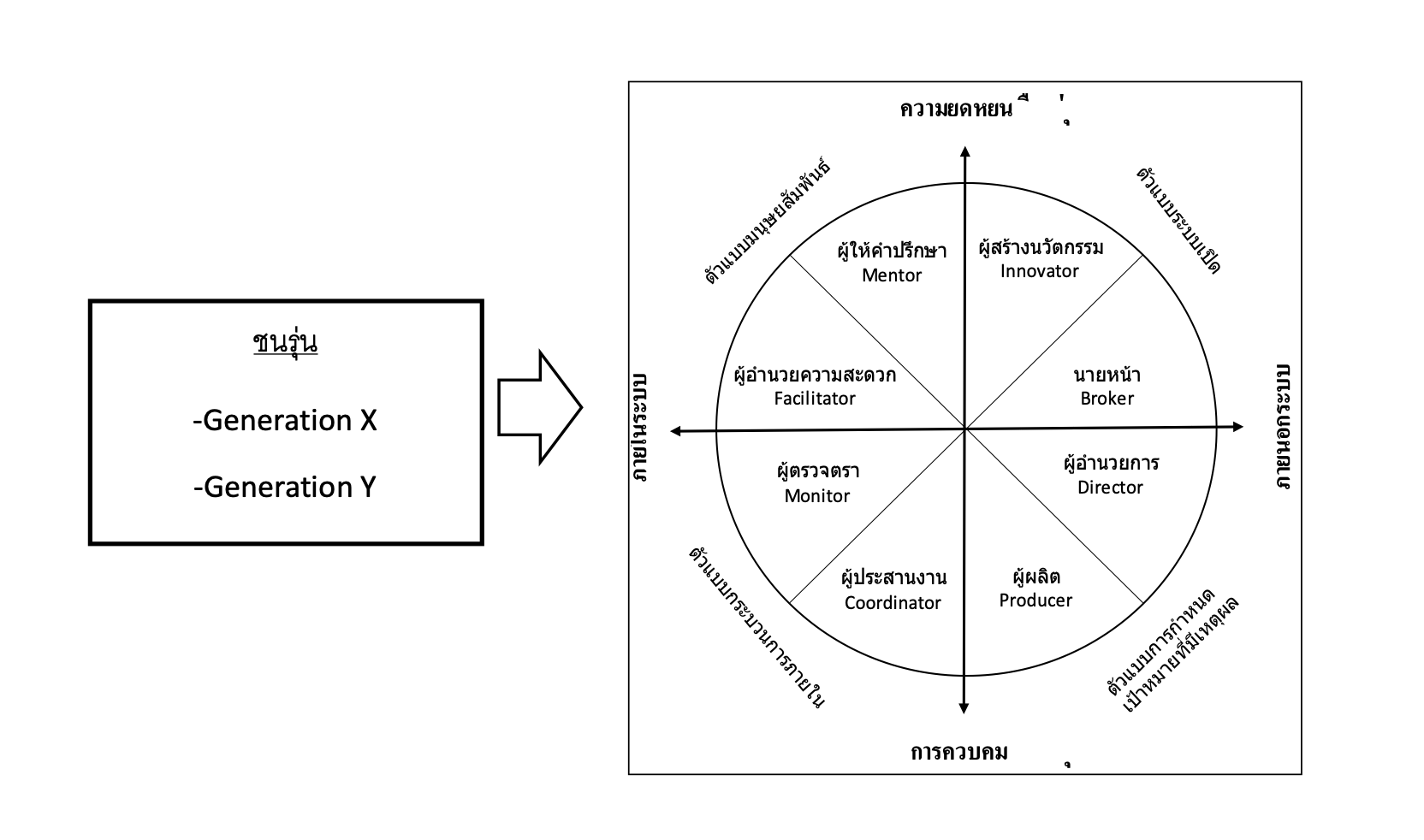
ชนรุ่นกับความเป็นผู้นำที่มีประสิทธิผล
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
การศึกษานี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อทดสอบการรับรู้ของพนักงานภาครัฐในแต่ละชนรุ่นเกี่ยวกับบทบาทความเป็นผู้นำที่มีประสิทธิภาพของผู้บริหารระดับกลาง คำถามการวิจัยคือ (1) ความเป็นผู้นำที่มีประสิทธิผลในความคาดหวังของผู้ปฏิบัติงานแต่ละชนรุ่นเป็นอย่างไร (2) ความเป็นผู้นำที่มีประสิทธิผลในความคาดหวังของผู้ปฏิบัติงานแต่ละชนรุ่นมีความแตกต่างกันหรือไม่? การศึกษานี้เป็นการวิจัยเชิงปริมาณ ใช้แบบสอบถามเพื่อวัดระดับบทบาทความเป็นผู้นำที่มีประสิทธิผลตามกรอบการแข่งขันค่านิยม Competing Values Framework (CVF) ของ Quinn โดยสุ่มตัวอย่างจากบุคลากรในหน่วยงานภาครัฐ จำนวน 227 คน
ผลการวิจัยพบว่า
มุมมองของบทบาทความเป็นผู้นำที่มีประสิทธิภาพมีความคล้ายคลึงกันระหว่างผู้ปฏิบัติงานแต่ละชนรุ่น โดยระดับคะแนนที่ 1 และ 2 ที่คาดหวังสำหรับทั้งชนรุ่น X และชนรุ่น Y คือบทบาทผู้อำนวยการ และผู้ผลิต นอกจากนี้ คะแนนลำดับที่ 3-5 ซึ่งเหมือนกันในแต่ละชนรุ่น เป็นบทบาทของผู้อำนวยความสะดวก, ผู้ประสานงาน และผู้สร้างนวัตกรรม แต่ชนรุ่น X ซึ่งอยู่ในลำดับที่ 5 เป็นเป็นนักประดิษฐ์ ส่วนชนรุ่น Y ผู้สร้างนวัตกรรมจะเลื่อนขึ้นมาอยู่ในลำดับที่ 3 และกลุ่มสุดท้ายในลำดับที่ 6-8 จะเป็นผู้ให้คำปรึกษา ผู้ตรวจตรา และนายหน้าเช่นเดียวกัน โดยทั้งสองชนรุ่นมีความคาดหวังต่อนายหน้าเป็นลำดับที่ 8 อันเป็นลำดับสุดท้ายเหมือนกัน ผลการวิจัยนี้จะเป็นข้อมูลที่ใช้ช่วยในการสร้างยุทธศาสตร์เพื่อเสริมสร้างประสิทธิผลองค์การ และช่วยในการวางแผนงานด้านการฝึกอบรมผู้บริหารระดับกลางในองค์การ
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
** ข้อความ ข้อคิดเห็น หรือข้อค้นพบ ในวารสารสหวิทยาการสังคมศาสตร์และการสื่อสารเป็นของผู้เขียน ซึ่งจะต้องรับผิดชอบต่อผลทางกฎหมายใด ๆ ที่อาจเกิดขึ้นจากบทความและงานวิจัยนั้น ๆ โดยมิใช่ความรับผิดชอบของคณะนิเทศศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏรำไพพรรณี **
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Anderson, H. J., Baur, J. E., Griffith, J. A., & Buckley, M. R. (2017). What works for you may not work for (Gen) Me: Limitations of present leadership theories for the new generation. The Leadership Quarterly, 28, 245–260.
Bass, B.M., (1990). From transactional to transformational leadership: Learning to share the vision. Organizational Dynamics,18(3), 19-31.
Burns, J.M. (1978). Leadership, Harper & Row. NY.
Cennamo, L. & Gardner, D. (2008). Generational Differences in Work Values, Outcomes, and Person-Organization Values fit. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 23, 891–906.
Deal, J. J., Stawiski, S., Gentry, W. A., & Cullen, K. L. (2014, 2 January). What makes a leader effective? U.S. boomers, Xers, and millennials weigh in [White paper]. https://www.ccl.org/wpcontent/uploads/2015/04/WhatMakesLeaderEffectiveUS.pd
Deninson D.R., Hooijberg R. & Quinn R.E., (1995). Paradox and performance: Toward a theory of behavioural complexity in managerial leadership, Organization science, 6(5), 524-540.
Drucker. P.F., (2005). Management: Tasks, responsibilities, practices. Truman Talley Books.
Fauziah, W., Yusoff, W. & Kian, T., (2013) Generation Differences in Work Motivation: From Developing Country Perspective. International Journal of Economy Management and Social Sciences, 2(4), 233-453.
Hair, J., Black, W., Babin, B., Anderson, R. and Tatham, R., (2006). Multivariate Data Analysis (6th Edition). Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Howe, N. & Strauss, B. (1993). 13th Gen: Abort, Retry, Ignore, Fail?. Vintage Books.
Howe, N. & Strauss, W. (2000). Millennials Rising: The Next Great Generation. Vintage Books.
Johnson, L. (2006). Mind Your X’s and Y’s: Satisfying the 10 Cravings of a New Generation of Consumers.Free Press.
Johnson, M., & Johnson, L. (2010). Generations, Inc: From Boomers to Linksters - Managing the friction between generations at work. AMACOM
Klein, K. (2004, April 15). “The ABCs of Selling to Generation X.” BusinessWeek.
Lancaster, L. & d. Stillman. (2002). When Generations Collide. Harper Collins.
Mannheim, K. (1952). The Problem of Generations. P. Kecskemeti. (ed.). Essays on the Sociology of Knowledge by Karl Mannheim. Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Quinn R.E. (1988). Beyond Rational Management, Mastering the Paradoxes and Competing Demands of High Performance, Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Quinn R.E. & Rohrbaugh J. (1983). A spatial model of effectiveness criteria: Towards a competing values approach to organizational analysis. Management Science, 29,(3), 23-45.
Ritchie, K. (1995). Marketing to Generation X. The Free Press.
Smith, W. S. (2008). Decoding Generational Differences. deloit development LLC.
Smola, K. W., & Sutton, C. D. (2002). Generational differences: Revisiting generational work values for the new millennium. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 23,363-382. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.147
Strauss, W. & Howe, N. (1991). Generations: The History of America’s Future, 1584 to 2069. Morrow.
Strauss, W. & Howe, N. (2007, March 30). Millennials as Graduate Students. Chronicle of Higher Education.
Van dyk, D. (2008, March 16) “Who’s Holding the Handbag? A new Generation of American Luxury Consumers is Telling mom what to Buy.” https://www.opdc.go.th/content/ODY.