GENERATIONS AND EFFECTIVE LEADERSHIP
Main Article Content
Abstract
The main objective of this study was to examine the perception of public employee in each generation about Effective leadership roles of their middle managers. The research questions are: (1) What is effective leadership role in the expectations of each generation of public employee? (2) Are there any different between generations? Quantitative study was employed by using questionnaires to measure the level of effective leadership role based on Quinn’s Competing Values Framework (CVF) approach. The sample was randomly drawn from government organizations, a total of 227 respondents.
The findings revealed that:
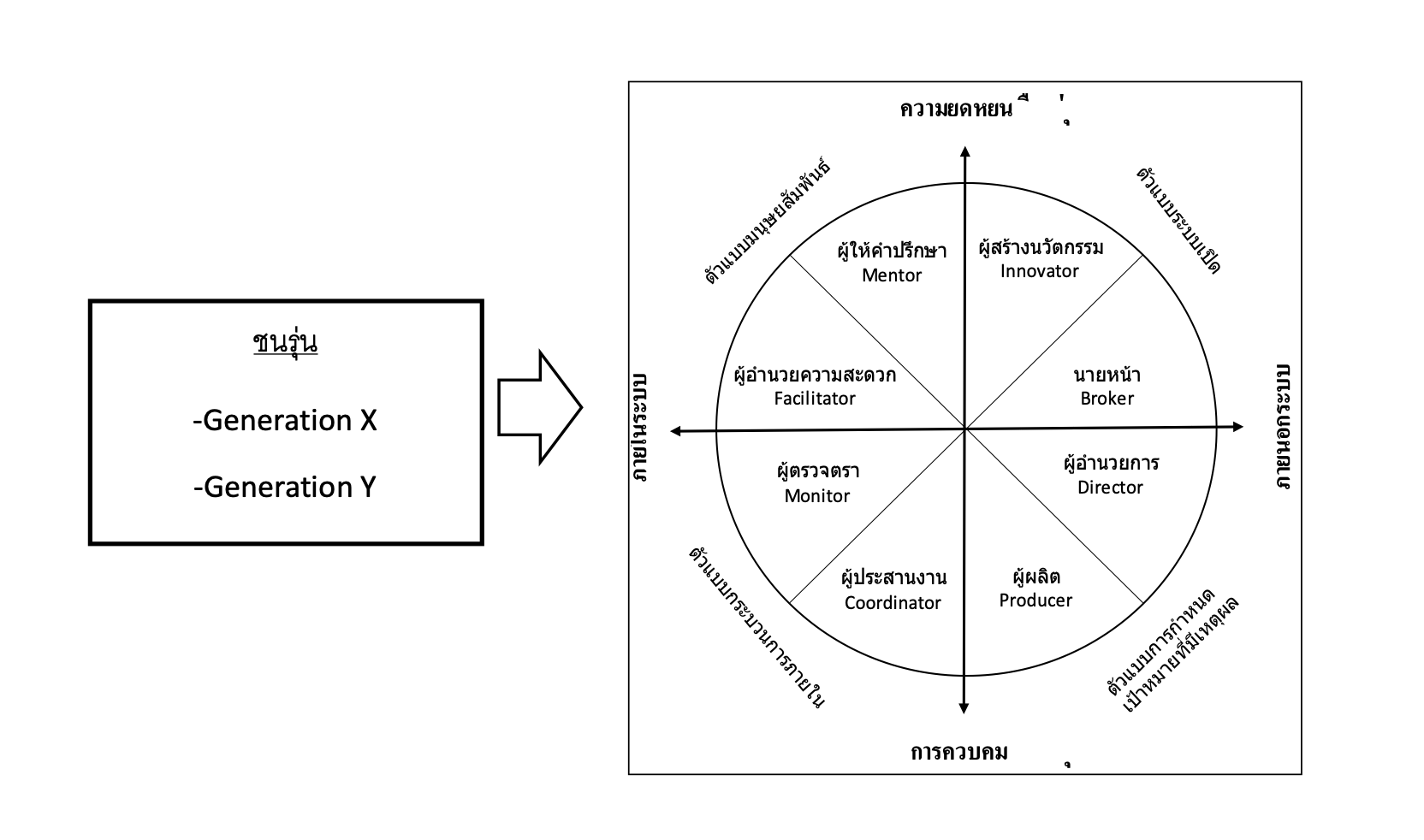
the viewpoints of effective leadership roles are similar among generations of employees. The 1st and 2nd score levels that were expected for both Gen X and Gen Y were Director and Producer role. Also, 3rd-5th scores levels; the Facilitator, Coordinator, and Innovator role are the same in each generation, but in Generation X, innovators are ranked 5th, in Generation Y, innovators move up to 3rd, and the last group in 6th-8th that are the Mentor, Monitor, and Brokers, also be the same. Meanwhile, both generations had the same expectations of Brokers as the last. The results of this research can be used to help create strategies for enhancing organizational effectiveness and in planning for the training course of middle-level executives in the organization.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The author(s) is only responsible for data appearing in the submitted manuscript of Interdisciplinary social sciences and communication journal.Besides, this journal encourages and enables you to share data such as statements, contents, figures, etc. that support your research publication where appropriate, and enables you to interlink the data with proper citation.
References
Anderson, H. J., Baur, J. E., Griffith, J. A., & Buckley, M. R. (2017). What works for you may not work for (Gen) Me: Limitations of present leadership theories for the new generation. The Leadership Quarterly, 28, 245–260.
Bass, B.M., (1990). From transactional to transformational leadership: Learning to share the vision. Organizational Dynamics,18(3), 19-31.
Burns, J.M. (1978). Leadership, Harper & Row. NY.
Cennamo, L. & Gardner, D. (2008). Generational Differences in Work Values, Outcomes, and Person-Organization Values fit. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 23, 891–906.
Deal, J. J., Stawiski, S., Gentry, W. A., & Cullen, K. L. (2014, 2 January). What makes a leader effective? U.S. boomers, Xers, and millennials weigh in [White paper]. https://www.ccl.org/wpcontent/uploads/2015/04/WhatMakesLeaderEffectiveUS.pd
Deninson D.R., Hooijberg R. & Quinn R.E., (1995). Paradox and performance: Toward a theory of behavioural complexity in managerial leadership, Organization science, 6(5), 524-540.
Drucker. P.F., (2005). Management: Tasks, responsibilities, practices. Truman Talley Books.
Fauziah, W., Yusoff, W. & Kian, T., (2013) Generation Differences in Work Motivation: From Developing Country Perspective. International Journal of Economy Management and Social Sciences, 2(4), 233-453.
Hair, J., Black, W., Babin, B., Anderson, R. and Tatham, R., (2006). Multivariate Data Analysis (6th Edition). Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Howe, N. & Strauss, B. (1993). 13th Gen: Abort, Retry, Ignore, Fail?. Vintage Books.
Howe, N. & Strauss, W. (2000). Millennials Rising: The Next Great Generation. Vintage Books.
Johnson, L. (2006). Mind Your X’s and Y’s: Satisfying the 10 Cravings of a New Generation of Consumers.Free Press.
Johnson, M., & Johnson, L. (2010). Generations, Inc: From Boomers to Linksters - Managing the friction between generations at work. AMACOM
Klein, K. (2004, April 15). “The ABCs of Selling to Generation X.” BusinessWeek.
Lancaster, L. & d. Stillman. (2002). When Generations Collide. Harper Collins.
Mannheim, K. (1952). The Problem of Generations. P. Kecskemeti. (ed.). Essays on the Sociology of Knowledge by Karl Mannheim. Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Quinn R.E. (1988). Beyond Rational Management, Mastering the Paradoxes and Competing Demands of High Performance, Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Quinn R.E. & Rohrbaugh J. (1983). A spatial model of effectiveness criteria: Towards a competing values approach to organizational analysis. Management Science, 29,(3), 23-45.
Ritchie, K. (1995). Marketing to Generation X. The Free Press.
Smith, W. S. (2008). Decoding Generational Differences. deloit development LLC.
Smola, K. W., & Sutton, C. D. (2002). Generational differences: Revisiting generational work values for the new millennium. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 23,363-382. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.147
Strauss, W. & Howe, N. (1991). Generations: The History of America’s Future, 1584 to 2069. Morrow.
Strauss, W. & Howe, N. (2007, March 30). Millennials as Graduate Students. Chronicle of Higher Education.
Van dyk, D. (2008, March 16) “Who’s Holding the Handbag? A new Generation of American Luxury Consumers is Telling mom what to Buy.” https://www.opdc.go.th/content/ODY.