Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: SWOT Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14456/educu.2024.46Keywords:
generative artificial intelligence, GenAI, AI in education, SWOT analysis, higher educationAbstract
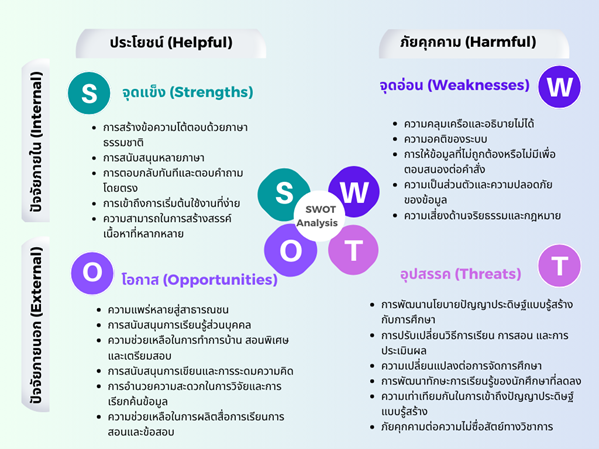
Generative artificial intelligence has rapidly spread to the public all over the world, reaching users in various industries, including education. The application of generative artificial intelligence in education presents both benefits and risks that impact higher education. Consequently, a thorough understanding and empirical data on generative artificial intelligence in education are essential. This study was therefore conducted utilizing the framework of SWOT analysis by searching, collecting, and examining relevant literature. The strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of generative artificial intelligence in higher education were analyzed and identified. The identified positive outcomes include: (1) strengths, namely the creation of interactive messages in natural language; support for multiple languages; instant replies and direct answers to questions; ease of access for beginners; and the capacity to generate diverse content; and (2) opportunities, namely widespread public accessibility; personalized learning support; assistance with homework; specialized tutoring and exam preparation; support for writing and brainstorming; facilitation of research and information retrieval; and aid in producing teaching materials and exams. Conversely, the identified negative outcomes include: (1) weaknesses, namely ambiguity and lack of explainability; system bias; incorrect or unavailable information in response to commands; privacy and data security issues; and ethical and legal risks; and (2) threats, namely the necessity to develop a generative artificial intelligence policy for education; modifications to teaching and assessment methods; changes to educational management; addressing the issue of declining learning skills among students; ensuring equal access to generative artificial intelligence; and combating the threat of academic dishonesty. These findings will be beneficial to students, teachers, educators, educational technology experts, and policymakers, as they provide a comprehensive analysis of both the benefits and threats of generative artificial intelligence in education. This analysis can inform the development of strategies for integrating generative artificial intelligence into higher education in the future.
References
Alasadi, E. A., & Baiz, C. R. (2023). Generative AI in Education and Research: Opportunities, Concerns, and Solutions. Journal of Chemical Education, 100(8), 2965–2971. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00323
Ali, K., Barhom, N., Tamimi, F., & Monty, D. (2023). ChatGPT—A double-edged sword for healthcare education? Implications for assessments of dental students. European Journal of Dental Education, 28(1), 206-211. https://doi.org/10.1111/eje.12937
Allam, H., Dempere, J., Akre, V., Parakash, D., Mazher, N., & Ahamed, J. (2023). Artificial Intelligence in Education: An Argument of Chat-GPT Use in Education. 2023 9th International Conference on Information Technology Trends (ITT). https://doi.org/10.1109/ITT59889.2023.10184267
Arcaute, G. M., Watson, L., Reviriego, P., Hern’andez, J. A., Juarez, M., and Sarkar, R. (2023). Combining generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet: Heading towards Evolution or Degradation? arXiv [Preprint]. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.2303.01255
Bahroun, Z., Anane, C., Ahmed, V., & Zacca, A. (2023). Transforming Education: A Comprehensive Review of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Educational Settings through Bibliometric and Content Analysis. Sustainability, 15(17), 12983. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712983
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2012). Thematic analysis. In H. Cooper, P. M. Camic, D. L. Long, A. T. Panter, D. Rindskopf, & K. J. Sher (Eds.), APA handbook of research methods in psychology, Vol. 2. Research designs: Quantitative, qualitative, neuropsychological, and biological (pp. 57–71). American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/13620-004
Capon, C. (2003). Understanding organisational context: Inside and outside organisations (2nd ed.). London: Financial Times/Prentice Hall.
Chan, C. K. Y. (2023). A comprehensive AI policy education framework for university teaching and learning. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00408-3
Chan, C. K. Y., & Hu, W. (2023). Students’ voices on generative AI: perceptions, benefits, and challenges in higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00411-8
Dai, Y., Liu, A., & Lim, C. P. (2023). Reconceptualizing ChatGPT and generative AI as a student-driven innovation in higher education. Procedia CIRP, 119, 84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2023.05.002
Ellis, A. R., & Slade, E. (2023). A New Era of Learning: Considerations for ChatGPT as a Tool to Enhance Statistics and Data Science Education. Journal of Statistics and Data Science Education, 31(2), 128–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/26939169.2023.2223609
Emenike, M. E., & Emenike, B. U. (2023). Was This Title Generated by ChatGPT? Considerations for Artificial Intelligence Text-Generation Software Programs for Chemists and Chemistry Educators. Journal of Chemical Education, 100(4), 1413-1418. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00063.
French, F., Levi, D., Maczo, C., Simonaityte, A., Triantafyllidis, S., Varda, G. (2023). Creative Use of OpenAI in Education: Case Studies from Game Development. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 7(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/mti7080081
Hsu, Y. C., & Ching, Y. H. (2023). Generative Artificial Intelligence in Education, Part One: the Dynamic Frontier. TechTrends, 67, 603–607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-023-00863-9
Jeon, J., & Lee, S. (2023). Large language models in education: A focus on the complementary relationship between human teachers and ChatGPT. Education and Information Technologies, 28, 15873–15892. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11834-1
Karabacak, M, O., Burak B., Margetis, K., Wintermark, M., & Bisdas, S. (2023). The Advent of Generative Language Models in Medical Education. JMIR medical education, 9, e48163. https://doi.org/10.2196/48163
Kelly, A., Sullivan, M., & Strampel, K. (2023). Generative artificial intelligence: University student awareness, experience, and confidence in use across disciplines. Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice, 20(6). https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.6.12
Kohnke, L., Moorhouse, B. L., & Zou, D. (2023). ChatGPT for Language Teaching and Learning. RELC Journal, 54(2), 537–550. https://doi.org/10.1177/00336882231162868
Kohnke, L., Moorhouse, B. L., & Zou, D. (2023). Exploring generative artificial intelligence preparedness among university language instructors: A case study. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 5, 100156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2023.100156
Leigh, D. (2010). SWOT Analysis. In R. Watkins & D. Leigh (Eds), Handbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace: Selecting and Implementing Performance Interventions. (pp. 115–140).
Mishra, P., Warr, M., & Islam, R. (2023). TPACK in the age of ChatGPT and Generative AI. Journal of Digital Learning in Teacher Education, 39(4), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/21532974.2023.2247480
Nikolic, S., Daniel, S., Haque, R., Belkina, M., Hassan, G. M., Grundy, S., Lyden, S., Neal, P., & Sandison, C. (2023). ChatGPT versus engineering education assessment: a multidisciplinary and multi-institutional benchmarking and analysis of this generative artificial intelligence tool to investigate assessment integrity. European Journal of Engineering Education, 48(4), 1–56. https://doi.org/10.1080/03043797.2023.2213169
Ratten, V., & Jones, P. (2023). Generative artificial intelligence (ChatGPT): Implications for management educators. The International Journal of Management Education, 21(3), 100857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2023.100857
Ray, P. P. (2023). ChatGPT: a Comprehensive Review on background, applications, Key challenges, bias, ethics, Limitations and Future Scope. Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems, 3(1), 121–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.04.003
Ruiz-Rojas, L. I., Acosta-Vargas, P., De-Moreta-Llovet, J., Gonzalez-Rodriguez, M. (2023). Empowering Education with Generative Artificial Intelligence Tools: Approach with an Instructional Design Matrix. Sustainability, 15(15), 11524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511524
Sullivan, M., Kelly, A., & McLaughlan, P. (2023). ChatGPT in higher education: Considerations for academic integrity and student learning. Journal of Applied Learning & Teaching, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.17
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. (2023). Guidance for generative AI in education and research. UNESCO. https://doi.org/10.54675/EWZM9535
Van Slyke, C., Johnson, R. D., & Sarabadani, J. (2023). Generative Artificial Intelligence in Information Systems Education: Challenges, Consequences, and Responses. Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 53(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.17705/1CAIS.05301
Walczak, K., & Cellary, W. (2023). Challenges for higher education in the era of widespread access to generative AI. The Poznań University of Economics Review, 9(2). https://doi.org/10.18559/ebr.2023.2.743
Yilmaz, R., & Yilmaz, F. G. K. (2023). Augmented intelligence in programming learning: Examining student views on the use of ChatGPT for programming learning. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans, 1(2), 100005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbah.2023.100005
Yu, H., & Guo, Y. (2023). Generative artificial intelligence empowers educational reform: current status, issues, and prospects. Frontiers in Education, 8, 1183162 https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2023.1183162
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



