แนวทางการเรียนรู้วิชาออกแบบสถาปัตยกรรมโดยใช้โจทย์โครงงานจริงและการบริการสังคมเป็นฐานเพื่อบูรณาการเทคนิคการก่อสร้างและความยั่งยืน
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
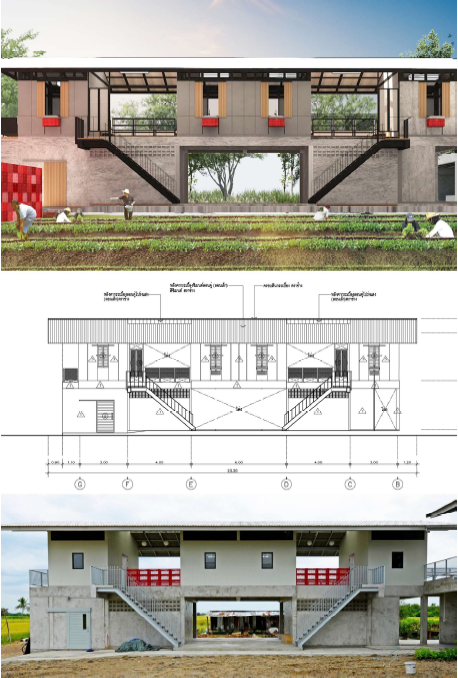
หลักสูตรการเรียนการสอนสถาปัตยกรรมปัจจุบัน มักพบปัญหาการเชื่อมต่อระหว่างแนวคิดในการออกแบบกับเทคนิคการก่อสร้าง ผลงานส่วนใหญ่ของรายวิชาปฏิบัติการออกแบบสถาปัตยกรรมจึงเป็นแบบร่างขั้นต้นหรือขั้นแนวคิดตามแต่ระดับความซับซ้อนของโครงการ การฝึกฝนให้นักศึกษาแปลงความคิดจากแบบร่างสู่แบบก่อสร้างจริงในหนึ่งภาคการศึกษาจึงดำเนินการจริงค่อนข้างยาก และกลายเป็นปัญหาของบัณฑิตที่ยังขาดความรู้ด้านเทคนิคการก่อสร้าง บทความนี้ จึงมีเป้าหมายที่จะเผยแพร่บทเรียนจากประสบการณ์การสอนสตูดิโอทางเลือก “Architectural detail studio” ของรายวิชาการออกแบบสถาปัตยกรรมขั้นสูง คณะสถาปัตยกรรมศาสตร์และการผังเมือง มหาวิทยาลัยธรรมศาสตร์ โดยได้ทดลองจัดกระบวนการเรียนรู้ที่บูรณาการงานออกแบบกับเทคนิคการก่อสร้าง โดยใช้โครงงานจริงและพัฒนาผลงานออกแบบทางสถาปัตยกรรมจนเป็นแบบก่อสร้างจริงเพื่อนำไปใช้ประโยชน์ในเวลาต่อมา การใช้โครงงานจริงเป็นฐานการเรียนรู้นี้ เป็นการประสานความร่วมมือระหว่างคณะวิชากับมูลนิธิหรือองค์กรเพื่อสาธารณะประโยชน์ภายนอก ซึ่งจัดเป็นการบริการสังคมอันเป็นนโยบายสำคัญของทางมหาวิทยาลัย ผลลัพธ์ของกระบวนการเรียนรู้นี้ได้ประเมินจากองค์ประกอบสำคัญ 3 ข้อของการเรียนรู้โดยใช้โครงสร้างเป็นฐาน ได้แก่ ประเด็นด้านการเรียนรู้ ด้านเนื้อหา และด้านสังคม ซึ่งบทเรียนดังกล่าวไม่ได้จะเป็นเพียงประโยชน์ในการศึกษานวัตกรรมการสอนสถาปัตยกรรม ที่ให้ความสำคัญกับการบูรณาการด้านเทคนิคการก่อสร้างในหลักสูตรวิชาชีพสถาปัตยกรรมแต่ยังสามารถเสริมสร้างจิตสำนึกสาธารณะแก่ผู้เรียนในเวลาเดียวกัน
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Association of Siamese Architects under the Royal Patronage (ASA). (2020). Architect Expo’20 “heritage in danger” design competition announcement. Retrieved December 29, 2020, from https://www.asaexpo.org /heritage-in-danger-competition
Barrows, H.S. & Tamblyn, R.M. (1980). Problem-based learning: an approach to medical education. New York: Springer Publishing Company.
Duch, B.J., Groh, S.E. & Allen, D.E. (2001). The power of problem-based learning. Virginia: Stylus Publishing.
Graaff, E. & Kolmos, A. (2007). History of problem-based and project-based learning. In Graaff, E. & Kolmos, A. (Ed.). Management of change: implementation of problem-based and project-based learning in engineering (pp.1-8). Rotterdam: Sense Publishers.
Grant, M.M. (2002). Getting a grip on project-based learning: theory, cases and recommendations. Meridian: A Middle School Computer Technologies Journal, 5(1), 1-17.
Jacoby, B. (1996). Service-learning in higher education: concepts and practices. San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Kolmos, A., et al. (2008). Facilitation in a PBL-environment. Retrieved August 1, 2021, from https://vbn.aau.dk/ws/portalfiles/portal/16177510/Facilitation_in_a_PBL_environment.pdf
Kuh, G.D. (2008). High-impact educational practices: what they are, who has access to them, and why they matter. Washington, D.C.: The American Association of Colleges and Universities (AAC&U).
Nanagara, Y. (2002). Nawattakam karn sueksa sathapattayakam. (In Thai) [Architectural education innovation]. Retrieved August 1, 2021, from http://pioneer.chula.ac.th/~yongyudh/book2/architectural-education-innovation-2.htm
Perez, S. (2000). Assessing service learning using pragmatic principles of education: a Texas charter school case study (Master’s thesis). San Marcos: Texas State University
Phattanawasin, S. (2018). Syllabus for AR 416 advanced architectural design (architectural detail studio unit) in semester 2/2017. Pathum Thani: Faculty of Architecture and Planning, Thammasat University.
Phattanawasin, S. (2022). Neawtang karnrianru wicha oakbab sathapattayakam doi chai chot khrongngan ching lae karnborikarn sangkhom pen than phuea buranakarn theknik karn kosang lae khwam yangyuen. (In Thai) [Architectural design learning approach using Real PBL and service learning for integrating construction techniques and sustainability] (Final report). Pathum Thani: Faculty of Architecture and Planning, Thammasat University.
Sigmon, R.L. (1997). Linking service with learning in liberal arts education. Washington, D.C.: Council for Independent Colleges.
Thammasat University. (2018). Thammasat mung songsoem karnrian karnson doi karn borikarn sangkhom. (In Thai) [Thammasat aims to promote teaching by social service learning]. Retrieved December 29, 2020, from https://tu.ac.th/thammasat-service-learning-2nd-semester-2560
Toole, J & Toole, P. (1995). Reflection as a tool for turning service experiences into learning experiences. In Toole, J. (Ed.). Enriching the curriculum through Service Learning (pp.99-114). San Francisco: Jossey Bass.