Predicting Urban Green Infrastructures of Ecosystem Services in Tehran Metropolitan Area Sprawl with Landsat Satellite time Series Data
Main Article Content
Abstract
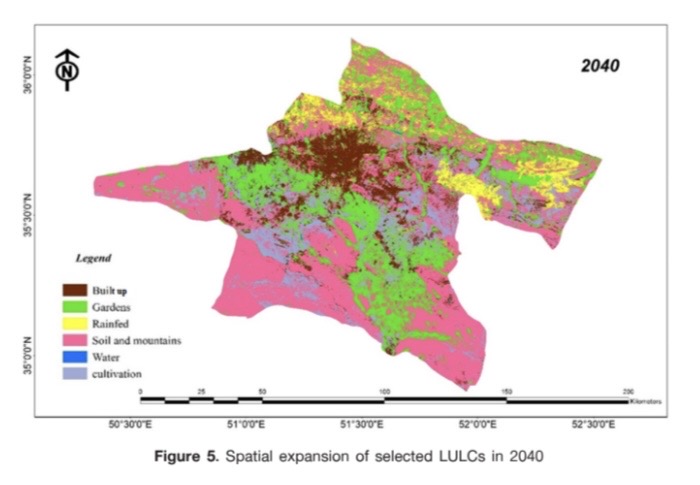
Urban green infrastructures play a crucial role in providing ecosystem services in metropolitan areas. However, the rapid urbanization and destruction of these infrastructures have become major concerns in the Tehran Metropolitan Region (TMR). This study focuses on analyzing the changes in Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) to highlight the significance of urban ecosystem services. The research utilized free Landsat time-series data from 2000, 2010, and 2020 to create a TMR development dataset. The study employed cellular automata and Markov chains to demonstrate the changes in LULC and the decline of urban green infrastructures in TMR. Six validated LULC classes were selected, including built up, garden, rainfed, soil and mountain, water, and cultivation. The data indicated that TMR’s agricultural development and urban green infrastructures have increased by 21% since 2000, reaching 45% in 2020, and are expected to grow by 43% of the TMR’s total LULC until 2040. The study highlights the potential risks of overusing lands for green infrastructure development, which have been as results of human activities by rapid urbanization, industrialization, and population growth. Furthermore, the growth of green infrastructure at the provincial level does not fully support TMR’s ecological capabilities. This study emphasizes the need for effective urban planning policies to ensure the sustainable development of urban green infrastructures and ecosystem services in metropolitan areas.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
All material is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0) License, unless otherwise stated. As such, authors are free to share, copy, and redistribute the material in any medium or format. The authors must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. The authors may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use. The authors may not use the material for commercial purposes. If the authors remix, transform, or build upon the material, they may not distribute the modified material, unless permission is obtained from JARS. Final, accepted versions of the paper may be posted on third party repositories, provided appropriate acknowledgement to the original source is clearly noted.
References
Aburas, M. M., Ho, Y. M., Ramli, M. F., & Ash’aari, Z. H. (2016). The simulation and prediction of spatio-temporal urban growth trends using cellular automata models: A review. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 52, 380-389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2016.07.007
Afifi, M. E. (2020). Modeling land use changes using Markov chain model and LCM model. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 20(56), 141-158. https://doi.org/10.29252/jgs.20.56.141
Ahmad, F., Goparaju, L., & Qayum, A. (2017). LULC analysis of urban spaces using Markov chain predictive model at Ranchi in India. Spatial Information Research, 25, 351–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41324-017-0102-x
Angélica, G. P. K., David, M. R., Domínguez-Amarillo, S., & Roberto, G. C. J. (2022). Remote sensing for the assessment of ecosystem services provided by urban vegetation. A review of the methods applied. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 127636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2022.127636
Ardalan, A., Khaleghy Rad, M., & Hadi, M. (2019). Urban water issues in the megacity of Tehran. In R.S. Bhaswati (Ed), Urban drought (pp. 263-288). Springer.
Bettencourt, L. M. A., Lobo, J., & Strumsky, D. (2023). Urban scaling and the loss of green spaces in global south cities. Environmental Research Letters, 18(3), 035001.
Bokaie, M., Zarkesh, M. K., Arasteh, P. D., & Hosseini, A. (2016). Assessment of urban heat island based on the relationship between land surface temperature and land use/land cover in Tehran. Sustainable Cities and Society, 23, 94-104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2016.03.009
Daba, M. H., & You, S. (2022). Quantitatively assessing the future land-use/land-cover changes and their driving factors in the upper stream of the Awash River based on the CA–markov model and their implications for water resources management. Sustainability, 14(3), 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031538
Darvishi, A., Yousefi, M., & Marull, J. (2020). Modelling landscape ecological assessments of land use and cover change scenarios. Application to the Bojnourd Metropolitan Area (NE Iran). Land Use Policy, 99, 105098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.105098
del Río-Mena, T., Willemen, L., Tesfamariam, G. T., Beukes, O., & Nelson, A. (2020). Remote sensing for mapping ecosystem services to support evaluation of ecological restoration interventions in an arid landscape. Ecological indicators, 113, 106182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106182
Dony, J. G., García, L. A. V., & Hernández, A. H. (2015). Green infrastructure and sustainable urbanism in Latin America. Landscape and Urban Planning, 132, 53-63.
Erdösy, George. (1995). The Indo-Aryans of ancient South Asia: Language, material culture and ethnicity. De Gruyter.
Esfandeh, S., Danehkar, A., & Salmanmahini, A. (2021). Simulation and prediction of urban growth pattern until 2050 using SLEUTH-3R model (Case study: coastal area of Parsian city). Journal of Environmental Studies, 47(1), 53-72. https://dx.doi.org/10.22059/jes.2021.324700.1008185
Falah, N., Karimi, A., & Harandi, A. T. (2020). Urban growth modeling using cellular automata model and AHP (case study: Qazvin city). Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 6(1), 235-248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00674-z
Fang, C., Sun, Z., & Wang, D. (2022). Urban green spaces and the livability of Chinese cities. Habitat International, 119, 102623.
Food and Agriculture Organization. (2021). Ecosystem Services & Biodiversity (ESB). Retrieved December 8, 2021, https://www.fao.org/ecosystem-services-biodiversity/news-events/news-details/en/c/1038435/
Farhadi, H., Faizi, M., & Sanaieian, H. (2019). Mitigating the urban heat island in a residential area in Tehran: Investigating the role of vegetation, materials, and orientation of buildings. Sustainable Cities and Society, 46, 101448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101448
Feng, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, S., & Tian, H. (2022). Spatiotemporal characteristics and driving factors of urban green space in global south metropolitans. Journal of Cleaner Production, 315, 128294.
Ghalehteimouri, K. J. (2024). Evaluate the capacity of Japanese spatial planning system for hazards integration realities and (f) acts: a pre-post the great east Japan Earthquake in Fukushima, 2011. Safety in Extreme Environments, 6, 201-218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42797-024-00102-1
Ghalehteimouri, K. J., Ros, F. C., & Rambat, S. (2024). Flood risk assessment through rapid urbanization LULC change with destruction of urban green infrastructures based on NASA Landsat time series data: A case of study Kuala Lumpur between 1990–2021. Ecological Frontiers, 44(2), 289-306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2023.06.007
Ghalehteimouri, K. J., Ros, F. C., Rambat, S., & Nasr, T. (2024). Spatial and temporal water pattern change detection through the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) for Initial flood assessment: A case study of Kuala Lumpur 1990 and 2021. Journal of Advanced Research in Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Sciences, 114(1), 178-187. https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.114.1.178187
Ghalehteimouri, K. J., Shamaei, A., & Ros, F. B. C. (2021). Effectiveness of spatial justice in sustainable development and classification of sustainability in Tehran province. Regional Statistics, 11(2). https://doi.org/10.15196/RS110201
Ghalehteimouri, K. J., Shamsoddini, A., Mousavi, M. N., Ros, F. B. C., & Khedmatzadeh, A. (2022). Predicting spatial and decadal of land use and land cover change using integrated cellular automata Markov chain model based scenarios (2019–2049) Zarriné-Rūd River Basin in Iran. Environmental Challenges, 6, 100399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100399
Ghoroghchian, N., Mirmohseni, M., & Nasiri-Kenari, M. (2019). Abnormality detection and monitoring in multi-sensor molecular communication. IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological and Multi-Scale Communications, 5(2), 68-83. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMBMC.2020.2979370
Gomes, L., Craveiro, D., & Freitas, D. (2022). An urban ecosystem services approach to assessing green infrastructure in global south metropolitans. Cities, 121, 103368.
Gómez-Baggethun, E., Tudor, M., Doroftei, M., Covaliov, S., Năstase, A., Onără, D. F., Mierla, M., Marinov, M., Dorosencu, A-C., Lupu, G., Teodorof, L., Tudor, I-M., Kohler, B., Museth, J., Aronsen, E., Johnsen, S.I., Ibram, O., Marin, E., Craciun, A., & Cioacă, E. (2019). Changes in ecosystem services from wetland loss and restoration: An ecosystem assessment of the Danube Delta (1960–2010). Ecosystem services, 39, 100965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2019.100965
Hosseini, S., Riahi, S., & Veysi, A. (2019). The effect of Urban Development on Watershed Hydrological Properties (case study: Tajrish Watershed). Journal of Spatial Analysis Environmental Hazards, 6(1), 95-110. http://dx.doi.org/10.29252/jsaeh.6.1.6
Hosseini, S. H., & Hosseini, M. (2016). Analysis of factors affecting Sprawl in urban areas of Iran. The Journal of Spatial Planning, 19(4), 33-66 http://hsmsp.modares.ac.ir/article-21-9461-fa.html
Ildoromi, A., Nori, H., Naderi, M., Amin, S. A., & Zeinivand, H. (2017). Land use change prediction using Markov chain and ca Markov model (Case study: Gareen watershed). Journal of Watershed Management Research, 8(16), 231-240. http://dx.doi.org/10.29252/jwmr.8.16.232
Jordan, S. J., Hayes, S. E., Yoskowitz, D., Smith, L. M., Summers, J. K., Russell, M., & Benson, W. H. (2010). Accounting for natural resources and environmental sustainability: Linking ecosystem services to human well-being. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(5), 1530-1536. https://doi.org/10.1021/es902597u
Kamusoko, C., Aniya, M., Adi, B., & Manjoro, M. (2009). Rural sustainability under threat in Zimbabwe–simulation of future land use/cover changes in the Bindura district based on the Markov-cellular automata model. Applied Geography, 29(3), 435-447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2008.10.002
Kandziora, M.., Burkhard, B., & Müller, F. (2013). Interactions of ecosystem properties, ecosystem integrity and ecosystem service indicators—A theoretical matrix exercise. Ecological Indicators, 28, 54-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.09.006
Kumar, S., Radhakrishnan, N., & Mathew, S. (2014). Land use change modelling using a Markov model and remote sensing. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 5(2), 145-156. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2013.795502
Lee, J., & Hong, Y. (2013). Urban green space, health, and well-being: A review of the literature. Health promotion perspectives, 3(1), 1-5.https://doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fdq068
Maleki, M., Malekani, L., & Valizadeh Kamran, K. (2020). Modeling occurrence and the spread of forest fire using cellular automata approach (Case Study: Arasbaran protected area). Journal of Natural Environment, 73(1), 129-141. https://dx.doi.org/10.22059/jne.2020.286679.1785
Matlhodi, B., Kenabatho, P. K., Parida, B. P., & Maphanyane, J. G. (2021). Analysis of the future land use land cover changes in the gaborone dam catchment using ca-markov model: Implications on water resources. Remote Sensing, 13(13), 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132427
Moghadam, H. S., & Helbich, M. (2013). Spatiotemporal urbanization processes in the megacity of Mumbai, India: A Markov chains-cellular automata urban growth model. Applied Geography, 40, 140-149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.01.009
Moradi, F., Kaboli, H. S., & Lashkarara, B. (2020). Projection of future land use/cover change in the Izeh-Pyon Plain of Iran using CA-Markov model. Arabian journal of geosciences, 13(19), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05984-6
Naddafi, K., Hassanvand, M. S., Yunesian, M., Momeniha, F., Nabizadeh, R., Faridi, S., & Gholampour, A. (2012). Health impact assessment of air pollution in megacity of Tehran, Iran. Iranian Journal Of Environmental Health Science & Engineering, 9(1), 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1735-2746-9-28
Najafi, V., Arbabi, A., & Adibi Sadinezhad, F. (2022). Investigation and analysis of various aspects of urban vulnerability due to drought in Tehran province. Iranian Journal of Ecohydrology, 8(4), 1045-1059. https://dx.doi.org/10.22059/ije.2021.333312.1574
Nasiri, V., Darvishsefat, A., Rafiee, R., Shirvany, A., & Hemat, M. A. (2019). Land use change modeling through an integrated multi-layer perceptron neural network and Markov chain analysis (case study: Arasbaran region, Iran). Journal of Forestry Research, 30(3), 943-957. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0659-9
Rabiner, L. R. (1989). A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 77(2), 257-286. https://doi.org/10.1109/5.18626
Rahnama, M. R. (2021). Forecasting land-use changes in Mashhad Metropolitan area using Cellular Automata and Markov chain model for 2016-2030. Sustainable Cities and Society, 64, 102548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102548
Romero, H., & Ordenes, F. (2004). Emerging urbanization in the Southern Andes. Mountain Research and Development, 24(3), 197-201. https://doi.org/10.1659/0276-4741(2004)024[0197:EUITSA]2.0.CO;2
Rosa, A., Santangelo, A., & Tondelli, S. (2021). Investigating the integration of cultural heritage disaster risk management into urban planning tools. The Ravenna case study. Sustainability, 13(2), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020872
Russo, A., & Cirella, G. T. (2020). Urban sustainability: Integrating ecology in city design and planning. In G.T. Cirella (Ed), Sustainable human–nature relations: Environmental scholarship, economic evaluation, urban strategies (pp. 187-204). Springer.
Sharifi, F., Nygaard, A., & Stone, W. M. (2021). Heterogeneity in the subjective well-being impact of access to urban green space. Sustainable Cities and Society, 74, 103244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103244
Sabzghabaei, G., Salehipour, F., Dashti, S., & Safavian, A. (2018). Land Use/Land Cover change modeling using Marcov chain and cellular Automata (Case Study: Dezful, Iran). Journal of Geography and Environmental Hazards, 7(2), 169-180. https://dx.doi.org/10.22067/geo.v7i2.64775
Salamat, S., Khaleghi, B., Imani, M., & Rosing, T. (2019). Workload-aware opportunistic energy efficiency in multi-fpga platforms. In 2019 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
Santé, I., García, A. M., Miranda, D., & Crecente, R. (2010). Cellular automata models for the simulation of real-world urban processes: A review and analysis. Landscape and Urban Planning, 96(2), 108-122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.03.001
Sejati, A. W., Buchori, I., & Rudiarto, I. (2018). The impact of urbanization to forest degradation in Metropolitan Semarang: A preliminary study. In IOP conference series: Earth and environmental science (Vol.123 no.1, p.012011). IOP Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/123/1/012011
Sharifi, S., Shahbazpanahi, S., & Dong, M. (2021). A POMDP-Based Antenna Selection for Massive MIMO Communication. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 70(3), 2025-2041. https://doi.org/10.15196/ RS110201 /10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3130198
Seto, K.C., Parnell, S., & Elmqvist, T. (2013). A Global outlook on urbanization. In T. Elmqvist, M. Fragkias, J. Goodness, B. Guneralp, P.J. Marcotullio, R.I. McDonald, S. Parnell, M. Schewenius, M. Sendstad, K. C. Seto & C. Wilkinson (Eds.), Urbanization, Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Challenges and Opportunities (pp. 1-12). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7088-1_1
Sohel, M. S. I., Mukul, S. A., & Burkhard, B. (2015). Landscape’s capacities to supply ecosystem services in Bangladesh: a mapping assessment for Lawachara National Park. Ecosystem Services, 12, 128–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2014.11.015
Statistical Center of Iran.(2021). [Data file]. Retrieved April 13, 2021, from https://www.amar.org.ir/Portals/1/yearbook/1397/03.pdf
Tobler, W.R. (1975) Linear operators applied to areal data..In Davis J.C. & McCullaugh M.J. (Eds.), Display and analysis of spatial data. (pp. 14–37). John Wiley & Sons.
Torrens, P. M. (2000). How cellular models of urban systems work (1. Theory) (CASA Working Papers 28). Centre for Advanced Spatial Analysis, University College London..
Vasiljević, N., Radić, B., Gavrilović, S., Šljukić, B., Medarević, M., & Ristić, R. (2018). The concept of green infrastructure and urban landscape planning: A challenge for urban forestry planning in Belgrade, Serbia. iForest-Biogeosciences and Forestry, 11(4), 491. https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor2683-011
Wrigley, N., & Bennett, R. J. (Eds.). (1981). Quantitative geography: A British view. Routledge.
Zangabadi, S. S., Shamsipour, A., Jafarpour Ghalehteimouri, K., & Hosseini, A. (2024). A holistic exploration local climate zoning through land use and land cover values: Tehran’s urban climate tapestry. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 155(12), 9783-9797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-024-05200-5