Design Research Methodology: Knowledge Inquiry Through Constructive Design Research
Main Article Content
Abstract
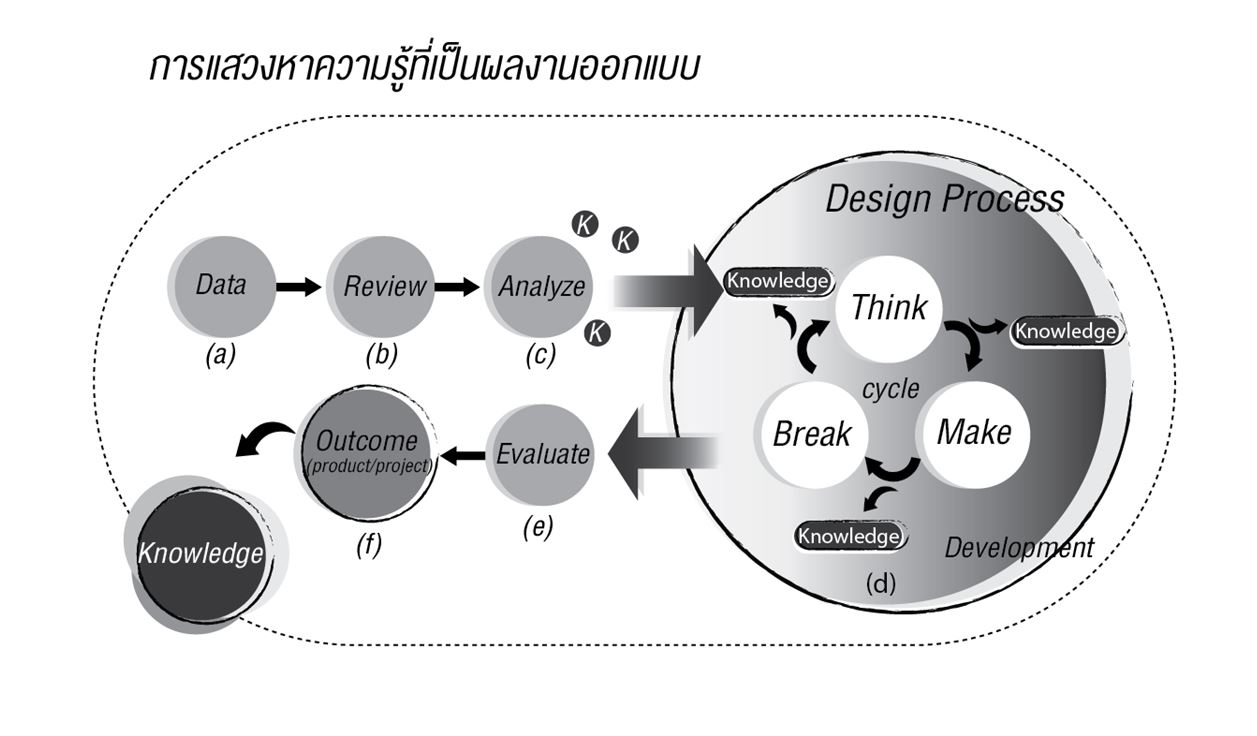
Design is a distinct discipline with mode of inquiry that different from science and humanities. It is a process with specific purpose with its own methodologies. Therefore, design output became a form of knowledge. In academia, design output is a form of research in various dimensions such as new knowledge that create transformation, problem solving for humanity, creating new perception and the exhibition of design output is a form of design knowledge distribution. Design research also play another role in transmitting knowledge back and forth between basic knowledge and society especially the research thorough design. The goal of “constructive design research” is to create through design process that results in 3 approaches as follows: 1) Design Practice Provides Methods, put design practice at the center of the research process and come up with new ways of using existing tools and creating new design tools that emphasizing on experiences and engagement; 2) Turn to Technology and Sandbox Culture, emphasizing on the selection of existing technologies and use engineering imagination to create prototype; 3) User Experience as Center of Design Research; emphasizing on emotional experience and empathy which widely use in leading design companies.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
All material is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0) License, unless otherwise stated. As such, authors are free to share, copy, and redistribute the material in any medium or format. The authors must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. The authors may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use. The authors may not use the material for commercial purposes. If the authors remix, transform, or build upon the material, they may not distribute the modified material, unless permission is obtained from JARS. Final, accepted versions of the paper may be posted on third party repositories, provided appropriate acknowledgement to the original source is clearly noted.
References
Archer, B. (1995). The Nature of Research. CoDesign, as transcribed by Rust in 2009
Cross, N. (2007a). Designerly Ways of Knowing. (Board of International Research in Design). Basel: Birkhäuser
Cross, N. (2007b). From a Design Science to a Design Discipline: Understanding Designerly Ways of Knowing and Thinking in Design In R. Michel (Ed.), Design Research Now. Basel: Birkhäuser.
Cross, N. (1982). Designerly ways of knowing. DESIGN STUDIES. 3(4), pp. 221-227
Downton, P. (2003). Design Research. Melburne: RMIT University Press.
Frayling, C. (1993). Research in Art and Design. Royal College of art Research Papers, 1(1), 1-5.
Gedenryd, H. (1998). How designers work: Cognitive studies. Lund: Lunduniversity
Horváth, I. (2007). Comparison of three methodological approaches of design research. INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ENGINEERING DESIGN, ICED’07. 28 - 31 August 2007, CITÉ DES SCIENCES ET DE L’INDUSTRIE, PARIS, FRANCE
Koskinen, I., Zimmerman, J., Binder, T., Redstrom, J., & Wensveen, S. (2011). Design Research Through Practice. From the Lab, Field, and Showroom. 1st Edition. morgan kaufmann.
Naiyapatana, O. (2011). Research Designs: Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Printing House.
Narvaez, L. M. J. (2000). Design’s own knowledge. Design Issues. 16(1) pp36-50.
Nelson, H. G. & Stolterman, E. (2003). The Design Way. New Jersey: Educational Technology Publications.
Owen, C. L. (1998). Design research: building the knowledge base. Design Studies, 19(1), 9-20
Simon, H. A. (1996). The sciences of the artificial (third edition). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Zimmerman, J. & Forlizzi, J. (2008). The Role of Design Artifacts in Design Theory Construction. Artifact, 2(1): 41-45